As the world grapples with the challenges of sustainable agricultural practices and environmental conservation, eco-friendly fertilizer production has emerged as a crucial aspect of modern farming. The overuse of chemical fertilizers in agriculture has led to significant environmental damage, such as soil degradation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, there has been a growing shift towards the production and use of eco-friendly fertilizers, which are not only safer for the environment but also more effective in maintaining soil health and improving crop yields. This article explores the progress of eco-friendly fertilizer production, focusing on the advances, benefits, and the role of new technologies in driving sustainability in agriculture.
What Are Eco-friendly Fertilizers?
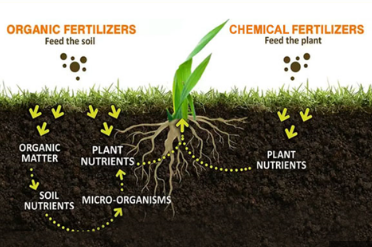
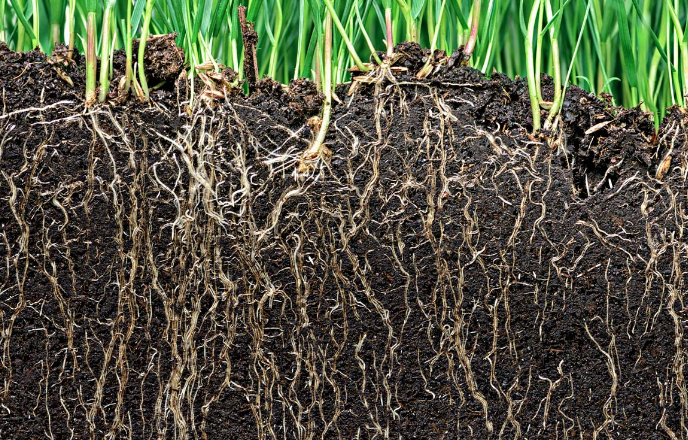
Eco-friendly fertilizers are fertilizers that promote plant growth without causing harm to the environment. These fertilizers are typically derived from natural, organic, or recycled sources and aim to replenish the nutrients in the soil while improving its structure and biological activity. Unlike traditional chemical fertilizers, which are often made from non-renewable resources, eco-friendly fertilizers are sustainable and can be produced with minimal environmental impact.
The main types of eco-friendly fertilizers include:
- Organic fertilizers: These are derived from natural sources like compost, manure, and plant residues. Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly, enhancing soil fertility over time.
- Bio-based fertilizers: These fertilizers contain living organisms such as beneficial bacteria, fungi, or algae that help improve soil nutrient availability and plant health.
- Recycled fertilizers: These fertilizers are produced from organic waste, such as food scraps, agricultural residues, or sewage sludge. By recycling organic matter, these fertilizers contribute to reducing waste and promoting sustainability in farming.
Recent Advancements in Eco-friendly Fertilizer Production
The production of eco-friendly fertilizers has made significant strides in recent years, driven by technological innovations, research, and a growing demand for sustainable agricultural practices. Several key developments have shaped the industry and paved the way for more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly fertilizers.
1. Sustainable Raw Materials

Compost Turner Working Site
One of the main challenges in eco-friendly fertilizer production is sourcing raw materials that are both sustainable and effective. Traditionally, fertilizers have been made from animal manure or other organic materials, but this can be limited by supply, land-use concerns, and potential contamination. Recent advances have focused on expanding the range of raw materials available for eco-friendly fertilizers.
For example, composting techniques have become more advanced, allowing a wider variety of organic waste, such as crop residues, food waste, and garden clippings, to be transformed into high-quality fertilizers. Additionally, biochar, a form of charcoal created from organic material, is gaining popularity as a sustainable fertilizer due to its ability to improve soil fertility and reduce carbon emissions.
2. Microbial Inoculants and Bio-fertilizers

The rise of microbial fertilizers is one of the most exciting developments in the eco-friendly fertilizer industry. Bio-based fertilizers use living organisms, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhizal fungi, and beneficial microbes, to improve the soil’s nutrient content and enhance plant growth. These microorganisms can help break down organic matter, fix nitrogen from the atmosphere, and promote nutrient cycling, reducing the need for synthetic chemical fertilizers.
For example, Rhizobium bacteria form symbiotic relationships with leguminous plants, fixing nitrogen into the soil, which is crucial for plant health. Similarly, mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic associations with plant roots, enhancing nutrient uptake, especially phosphorus. Bio-fertilizers not only improve soil health but also contribute to reduced dependency on chemical fertilizers, reducing their negative environmental impact.
3. Slow-Release Fertilizers
Slow-release fertilizers are another significant innovation in eco-friendly fertilizer production. These fertilizers release nutrients gradually over time, providing a more consistent supply of nutrients to plants and minimizing nutrient loss due to leaching or runoff. Slow-release fertilizers help improve fertilizer efficiency by allowing nutrients to be available to plants over extended periods, reducing the frequency of application and minimizing the environmental impact.
Recent advancements in coating technologies have enabled the development of more efficient slow-release fertilizers. Polymer coatings, for example, are used to encase the nutrients, controlling their release rate and ensuring that the nutrients are available when plants need them most. This results in lower fertilizer use and reduced environmental contamination.
4. Waste-to-Fertilizer Technologies

Compost Processing Crushing
As the world moves toward a circular economy, the recycling of organic waste into fertilizers has become a prominent solution in eco-friendly fertilizer production. Technologies that convert agricultural, industrial, and municipal waste into fertilizers help reduce waste accumulation while providing farmers with affordable and sustainable fertilizer options.
For instance, anaerobic digestion processes break down organic waste, such as food scraps and livestock manure, to produce biogas and compost, which can be used as fertilizers. Similarly, vermicomposting, which involves the use of earthworms to break down organic matter, is gaining popularity as a way to produce nutrient-rich organic fertilizers.
5. Nano-Technology in Fertilizer Production
One of the most recent advancements in eco-friendly fertilizer production is the use of nanotechnology. Nanomaterials are being used to enhance fertilizer efficiency by improving nutrient delivery, reducing nutrient loss, and increasing plant uptake. For instance, nano-encapsulated fertilizers can release nutrients in a controlled manner, ensuring that plants receive the nutrients they need over a longer period.
Nanotechnology also enables the development of fertilizers that are more efficient at targeting specific plant needs. By using nanoparticles, nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium can be more easily absorbed by plants, leading to improved growth and productivity.
Benefits of Eco-friendly Fertilizer Production
The transition to eco-friendly fertilizers offers numerous benefits for both the environment and agricultural productivity. Some of the main advantages include:
1. Reduced Environmental Impact
Eco-friendly fertilizers have a much lower environmental impact compared to traditional synthetic fertilizers. They minimize nutrient runoff, which reduces water pollution and eutrophication in nearby water bodies. Additionally, eco-friendly fertilizers improve soil structure, helping to reduce soil erosion and desertification.
2. Improved Soil Health
Unlike chemical fertilizers, which can degrade soil health over time, eco-friendly fertilizers enhance soil fertility by adding organic matter and supporting beneficial microbial activity. This promotes healthier soils, improves water retention, and increases long-term soil productivity.
3. Increased Nutrient Use Efficiency
By releasing nutrients gradually, slow-release fertilizers and bio-fertilizers improve nutrient use efficiency. This means that plants can access nutrients more effectively, leading to better growth and higher yields with reduced fertilizer input.
4. Sustainability and Resource Efficiency
Eco-friendly fertilizers contribute to the sustainability of farming by using renewable resources and reducing the dependence on non-renewable chemical inputs. Waste-to-fertilizer technologies also contribute to reducing agricultural waste, providing a sustainable solution to waste disposal.
Conclusion
The progress of eco-friendly fertilizer production has been driven by a combination of technological innovations, sustainability goals, and growing environmental concerns. As more farmers and agricultural businesses seek to adopt sustainable practices, eco-friendly fertilizers offer a viable and effective solution. With continued research and development in areas such as microbial inoculants, slow-release fertilizers, and waste recycling, the future of fertilizer production is both environmentally and economically sustainable.
By embracing these advances in eco-friendly fertilizer production, farmers can help meet the growing demand for food while minimizing their environmental footprint, ensuring that agriculture remains a key contributor to a sustainable future.






Get A Quote