Overview of the NPK Fertilizer Production System
The NPK fertilizer production system is a complete workflow designed to produce high-quality, nutrient-rich compound fertilizer. This system combines multiple processes to convert raw materials such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium into uniform granules suitable for modern agriculture. By integrating advanced equipment and careful process control, factories can achieve consistent fertilizer quality, reduce waste, and maintain efficient production. In this guide, we explain the nine key steps of a typical NPK fertilizer production system, highlighting both equipment and operational considerations.
Step 1: Batching System
The production process begins with a batching system, where raw materials are accurately measured according to the required NPK ratio. Precise batching is critical for nutrient uniformity. Modern batching systems use electronic load cells and automated control, reducing human error and ensuring each batch meets the target nutrient composition. Proper batching sets the foundation for a consistent NPK fertilizer production system.
Step 2: Feeding
After batching, materials are transferred to the production line through a feeding system. The most commonly used feeding system is the bucket elevator. Feeders regulate the flow of raw materials into the mixer, ensuring continuous and uniform input. Consistent feeding prevents blockages and ensures that each component is properly incorporated, maintaining the overall efficiency of the NPK fertilizer production system.
Step 3: Mixing
In the mixing stage, raw materials are blended thoroughly to achieve even distribution of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Efficient mixing is essential for nutrient consistency across all granules. Double shaft mixers and horizontal mixers are recommended for mixing equipment. High-performance mixers shorten blending time while ensuring homogeneity, which is crucial for the fertilizer’s performance in agricultural applications.
Step 4: Granulation
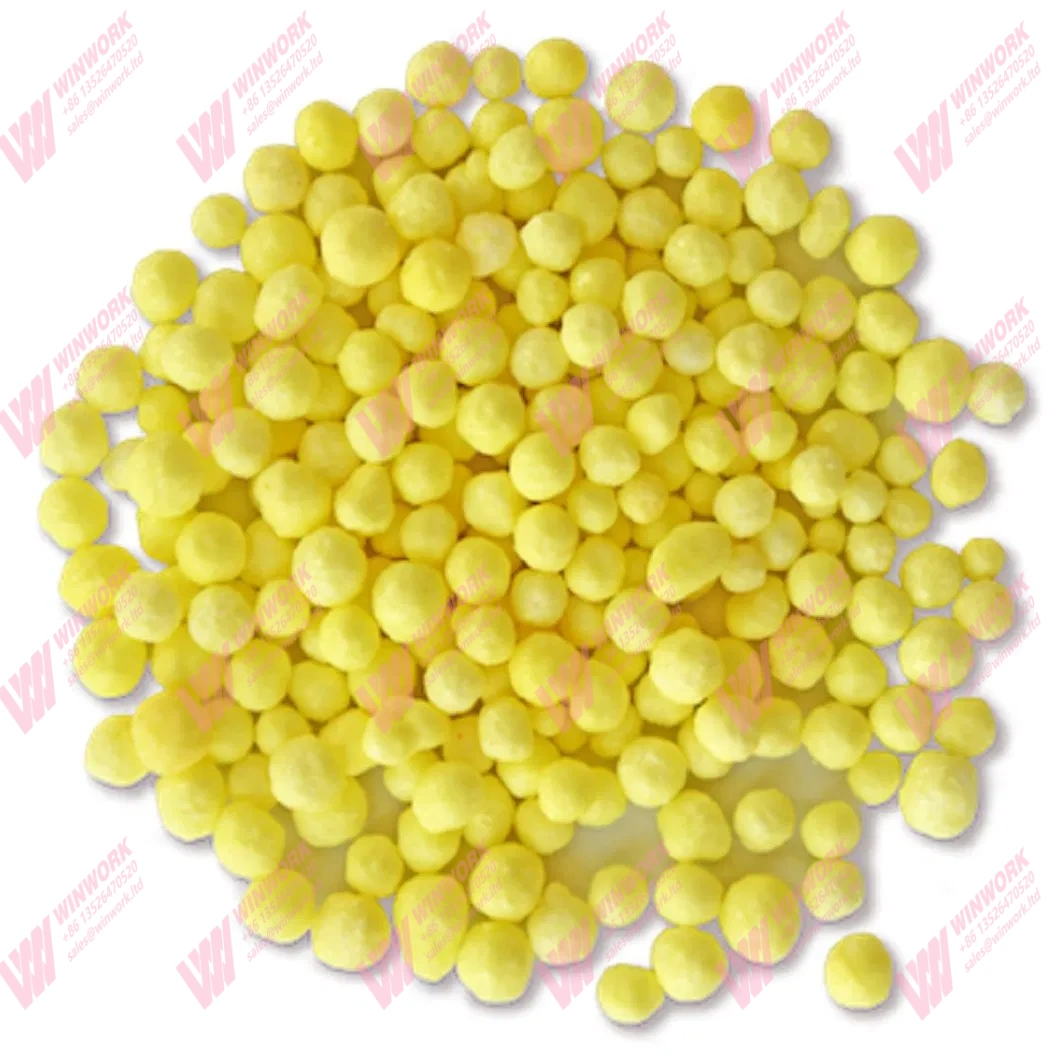
The blended material is then shaped into granules using a granulator. This step determines the granule size, density, and durability. Common types include rotary drum granulators, disc granulators, and high-speed double roller extrusion granulators. Proper granulation ensures nutrient retention, uniformity, and ease of handling in subsequent processing steps.
Step 5: Drying
Granules contain moisture after granulation. A dryer reduces water content to the desired level, preventing caking and microbial growth. Correct temperature control during drying preserves nutrient content and granule integrity, which is essential for long-term storage and transport in the NPK fertilizer production system.
Step 6: Cooling
After drying, granules pass through a cooling machine. Cooling stabilizes granules, reduces thermal stress, and minimizes breakage. This step ensures uniform size, density, and structural integrity, preparing the product for screening and further processing.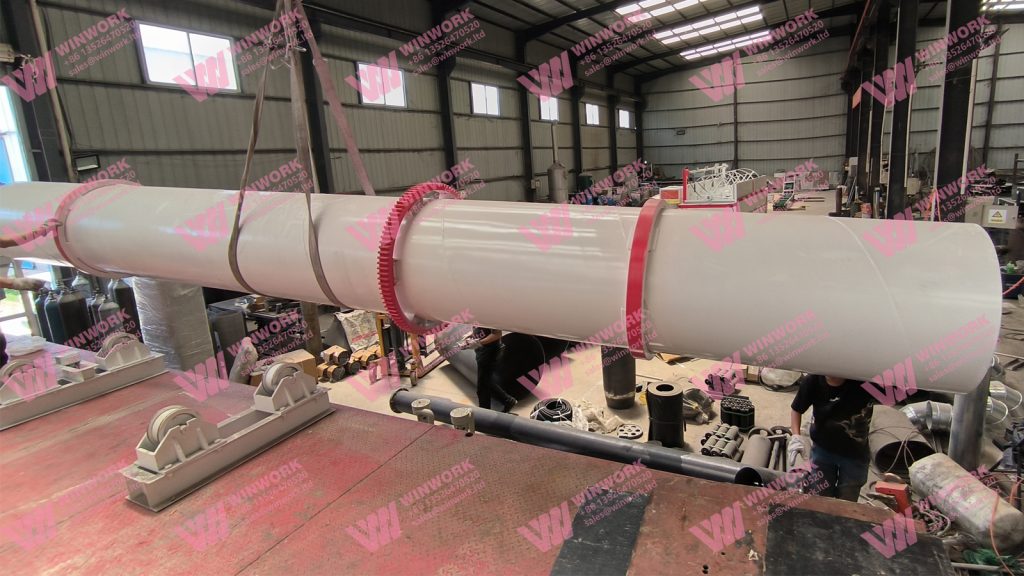
Step 7: Screening
A screen machine separates granules that do not meet size requirements. Oversized and undersized granules are returned to the granulator for recycling. Screening is critical to maintain product uniformity and ensures that only properly sized granules reach the coating and packaging stages.
Step 8: Coating
During the coating stage, granules are treated with anti-caking agents or protective coatings. Coating reduces dust, enhances storage stability, and preserves nutrient availability. This step is particularly important for long-term storage or fertilizers destined for export markets, as it improves durability and handling safety.
Step 9: Packaging and Maintenance Considerations
The final step combines automatic packaging with key operational practices. Granules are weighed, sealed, and packed efficiently using automatic machines. Proper packaging prevents contamination and moisture ingress. Additionally, manufacturers should prioritize regular equipment maintenance and raw material inspection at this stage. Keeping mixers, granulators, dryers, coolers, and sieving machines in optimal condition reduces downtime, prolongs equipment life, and ensures consistent quality throughout the NPK fertilizer production system.
Key Insights for Efficient NPK Fertilizer Production
A successful NPK fertilizer production system depends on both equipment and process optimization:
-
Raw Material Quality – Use high-quality nitrogen, phosphate, and potassium sources to ensure consistent nutrient content.
-
Process Monitoring – Track temperature, moisture, and mixing times to maintain granule uniformity.
-
Recycling Granules – Return off-spec granules to the granulator to reduce waste and improve yield.
-
Energy Efficiency – Optimize dryers and coolers for minimal energy use without compromising quality.
-
Scalability – Modular equipment allows flexible capacity expansion.
-
Preventive Maintenance – Routine inspection of all equipment reduces downtime and supports continuous production.
By combining these practices with modern equipment, advanced process monitoring, and careful quality control, manufacturers can produce uniform, nutrient-rich NPK fertilizer granules efficiently, reliably, and consistently for both domestic and international agricultural markets.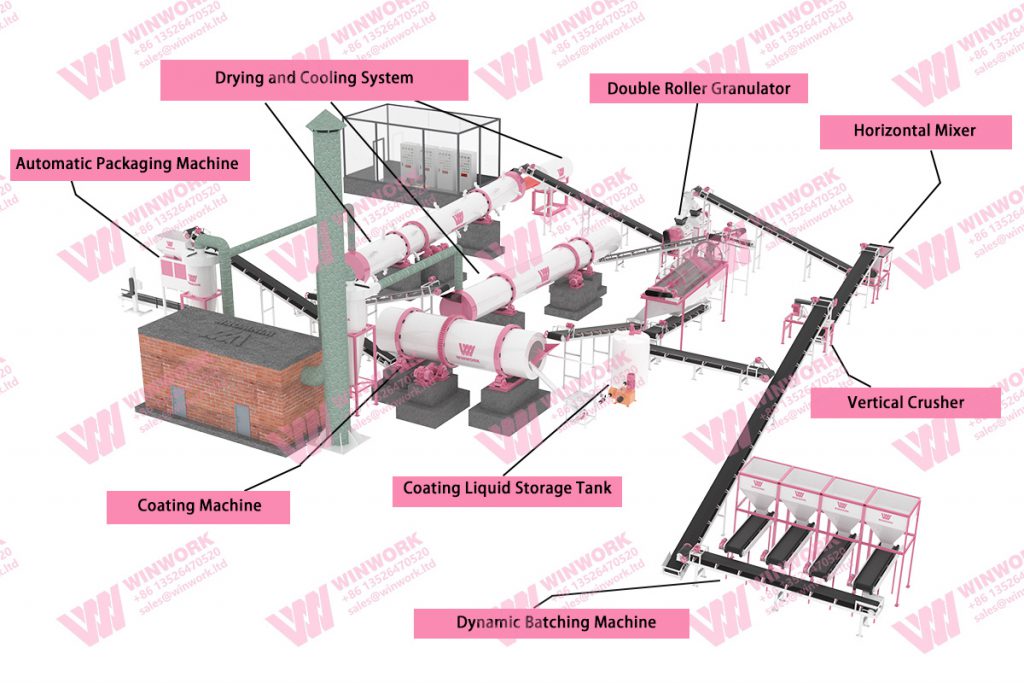
Conclusion
The NPK fertilizer production system is a multi-step process that ensures high-quality granules suitable for agricultural applications. From batching, feeding, and mixing, to granulation, drying, cooling, screening, coating, and packaging, each stage is essential for maintaining product quality and operational efficiency. Focusing on raw material selection, equipment maintenance, and process optimization allows manufacturers to operate a reliable NPK fertilizer production system, producing fertilizer that meets domestic and international standards while maximizing productivity and minimizing operational costs.
For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Email: sales@lanesvc.com
Contact number: +86 13526470520
Whatsapp: +86 13526470520






Get A Quote