Asia, home to more than half of the world’s population, faces growing challenges in balancing agricultural production with environmental sustainability. As the demand for food increases, driven by rapid population growth and urbanization, traditional chemical fertilizers have raised concerns over their long-term impact on soil health, water resources, and biodiversity. Consequently, the shift towards organic fertilizer plants is becoming an essential part of Asia’s agricultural landscape.
This article explores the role of organic fertilizer plants for Asia, the benefits they bring to the region, and how they help address the challenges of sustainable agriculture while enhancing food security.
The Need for Organic Fertilizer in Asia
The rapid expansion of industrial agriculture in Asia has been accompanied by an over-reliance on chemical fertilizers. While these fertilizers have boosted crop yields in the short term, their long-term impact on soil quality, water pollution, and human health is raising alarms. Problems like soil acidification, nutrient imbalances, and the contamination of water bodies with nitrogen and phosphorus have led to growing interest in more sustainable farming practices.
Organic fertilizers, made from natural or recycled materials such as animal manure, crop residues, and compost, offer a viable alternative. These fertilizers not only replenish the soil with essential nutrients but also help maintain its health and structure over time. Given Asia’s large agricultural base, an increasing demand for eco-friendly farming solutions has led to the development of dedicated organic fertilizer plants that serve both local and regional markets.
What Makes Organic Fertilizer Plants Unique?
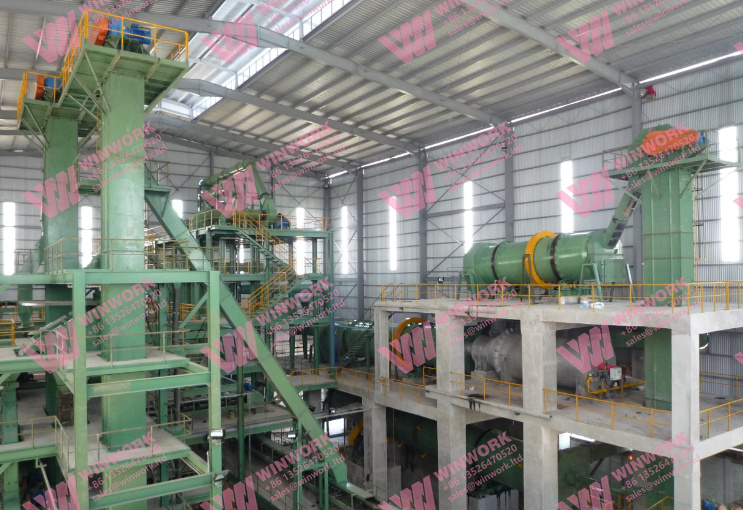
Unlike chemical fertilizers, which provide immediate nutrient release, organic fertilizers have the unique ability to improve soil health and fertility over the long term. Organic fertilizer plants play a vital role in this by producing fertilizers that release nutrients slowly and improve the soil’s microbial activity. Here’s a closer look at what makes these plants so critical for sustainable agriculture in Asia:
1. Raw Material Sourcing
Organic fertilizer production relies heavily on locally sourced materials, such as:
- Animal Manure: Livestock waste, including cow, chicken, and horse manure, is composted and processed to make organic fertilizers. These materials are abundant in Asia, especially in rural and agricultural regions.

- Plant Residues: Crop residues from rice, wheat, sugarcane, and other staple crops are often repurposed as organic fertilizers. This not only provides nutrients to the soil but also helps in recycling agricultural waste.
- Food Waste and Organic Waste: With rapidly growing cities across Asia, organic waste, including food scraps, is increasingly being recycled to produce organic fertilizers. This contributes to waste reduction and resource efficiency.
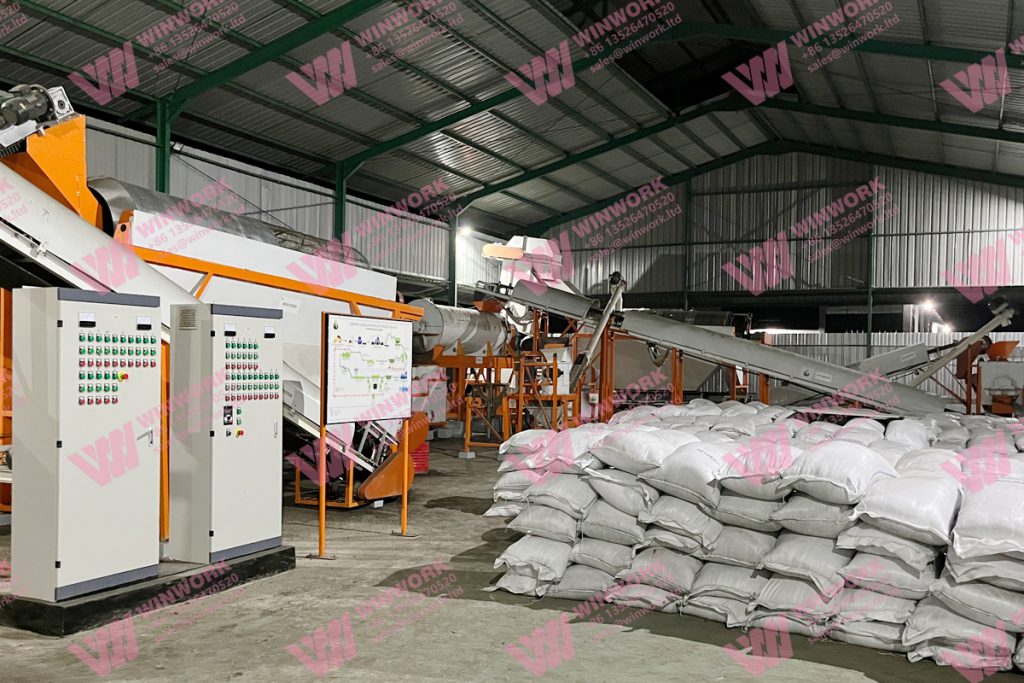
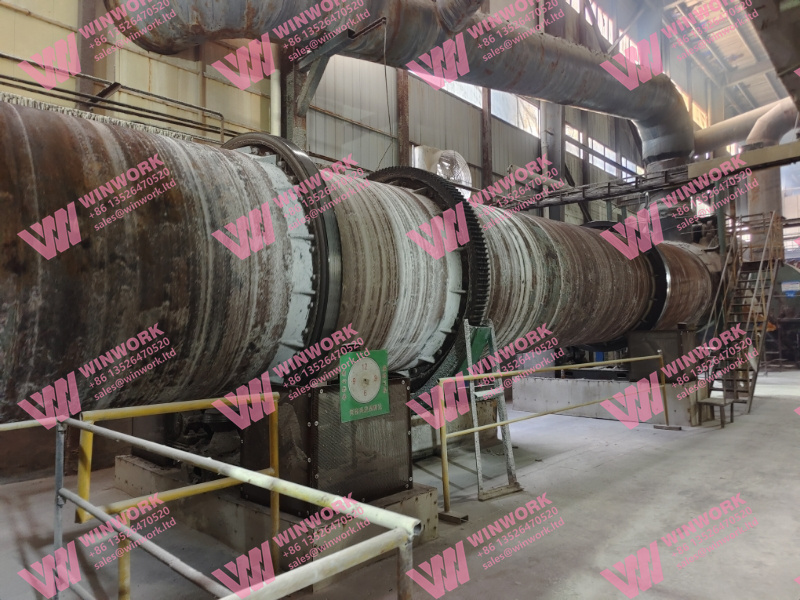
2. Sustainable Production Techniques
Modern organic fertilizer plants utilize sustainable production techniques that reduce carbon emissions, conserve energy, and minimize waste. Technologies such as aerobic and anaerobic composting, vermicomposting, and biogas production are commonly used in these plants. They not only help in producing high-quality fertilizers but also contribute to a more sustainable agricultural ecosystem by:
- Reducing methane emissions from agricultural waste.
- Converting organic waste into valuable soil amendments.
- Producing biogas as a by-product, which can be used for energy generation.
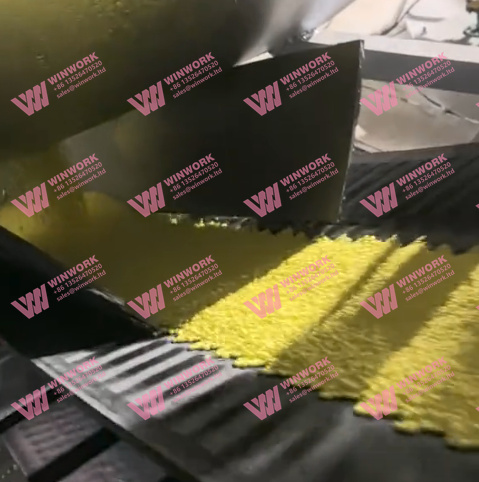
3. Nutrient-Rich Fertilizer Formulations
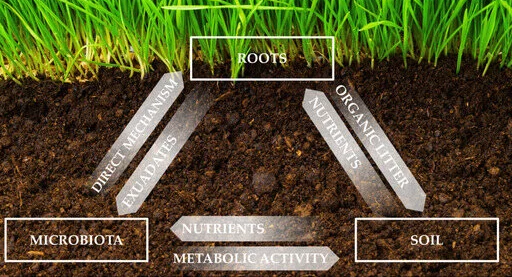
The fertilizers produced by organic fertilizer plants are typically rich in macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) as well as micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. More importantly, they contain humic substances and micronutrients that help improve soil structure and fertility. These fertilizers are slow-release, meaning that the nutrients are made available to plants gradually, promoting healthier and more resilient crops over time.
Additionally, many organic fertilizers contain beneficial microorganisms that promote soil health by enhancing nutrient uptake, decomposing organic matter, and suppressing harmful pathogens. These beneficial microbes are particularly valuable for improving soil microbial diversity, which is essential for long-term soil productivity.
Why is Organic Fertilizer Production Important for Asia?
Asia’s diverse agricultural needs present unique challenges when it comes to fertilizer production. Here’s why organic fertilizer plants are crucial for the region:
1. Soil Degradation and Desertification

Many parts of Asia are grappling with soil degradation and desertification, often as a result of overuse of chemical fertilizers and poor agricultural practices. Organic fertilizers help reverse these processes by improving soil texture, water retention, and microbial activity. By restoring soil health, organic fertilizers play a key role in ensuring long-term agricultural productivity.
2. Sustainable Farming Practices
As Asian countries become more aware of the environmental impact of traditional chemical fertilizers, governments and agricultural organizations are promoting sustainable farming practices. Organic fertilizer plants are at the forefront of this transition, providing farmers with safe, environmentally-friendly alternatives that help improve both crop yield and soil health.
3. Waste Reduction and Resource Recycling
Organic fertilizer production from waste materials such as agricultural residues, food scraps, and livestock manure is a highly sustainable practice that helps reduce waste and close the loop in agricultural production systems. This waste-to-fertilizer process reduces the environmental burden associated with waste disposal, while providing farmers with affordable and high-quality fertilizers.
4. Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Traditional chemical fertilizers contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions through processes like the release of nitrous oxide. Organic fertilizers, by contrast, have a much lower carbon footprint, making them an essential part of the region’s efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce agricultural emissions.
5. Healthier and Safer Crops

Organic fertilizers contribute to the production of crops that are free from harmful chemical residues. This is particularly important in Asia, where the demand for organic produce is increasing due to growing health concerns. By using organic fertilizers, farmers can ensure that their crops are healthier, more nutritious, and safer for human consumption.
Challenges Facing Organic Fertilizer Production in Asia
Despite the growing adoption of organic fertilizers, there are still several challenges to the widespread use of organic fertilizer plant in Asia:
1. High Initial Investment
Setting up an organic fertilizer plant requires significant initial investment in machinery, technology, and infrastructure. The process of collecting, composting, and processing organic waste can also be labor-intensive and costly. However, governments and NGOs are increasingly providing subsidies and financial support to encourage farmers and businesses to adopt organic farming practices.
2. Market Awareness and Acceptance
While organic fertilizers are gaining popularity, many farmers in Asia remain skeptical about their efficacy and cost-effectiveness. There is a need for greater education and awareness about the long-term benefits of organic fertilizers, including improved soil health and sustainable farming practices.
3. Logistical Challenges
The logistics of sourcing raw materials, especially in rural and remote areas, can be challenging. In some regions, transportation costs and the availability of waste materials can impact the production of organic fertilizers. Nevertheless, innovations in local collection networks and waste-to-fertilizer systems are helping overcome these challenges.
Conclusion
The development of organic fertilizer plants in Asia represents a significant step forward in the region’s journey towards more sustainable and environmentally-friendly agriculture. By producing nutrient-rich, slow-release fertilizers from locally sourced organic materials, these plants contribute to healthier soils, higher crop yields, and a reduction in agricultural waste. As the demand for sustainable farming practices grows, the role of organic fertilizers in ensuring food security, promoting environmental conservation, and improving the livelihoods of farmers will become even more critical in Asia’s agricultural future.







Get A Quote