In the age of sustainable agriculture, the demand for soil-friendly, eco-safe fertilization solutions is stronger than ever. Among the most promising innovations is humic acid organic fertilizer, a bio-based soil amendment that plays a pivotal role in improving soil fertility, nutrient availability, and crop productivity. This article explores how humic acid fertilizers work, their advantages, production processes, and applications in modern farming.
What is Humic Acid Organic Fertilizer?
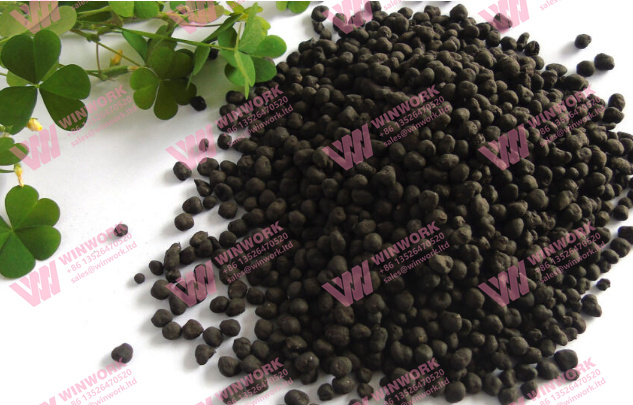

Humic acid is a complex mixture of organic molecules derived from the decomposition of plant and animal matter. These substances are naturally found in soil, peat, and lignite, but can also be industrially extracted and concentrated for agricultural use.
When processed into organic fertilizer, humic acid becomes a powerful soil conditioner and nutrient enhancer, promoting microbial activity and boosting plant nutrient uptake.
How Humic Acid Works in Soil
Humic acid improves soil properties in several ways:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chelation of Nutrients | Enhances absorption of micronutrients like Fe, Zn, Cu |
| Soil Aggregation | Improves water retention and aeration |
| pH Buffering | Neutralizes soil acidity and alkalinity |
| Microbial Activation | Stimulates beneficial soil microbes |
| Root Growth Enhancement | Promotes stronger and deeper root systems |
These benefits lead to more resilient crops, reduced chemical fertilizer dependency, and improved soil structure over time.
Production of Humic Acid Organic Fertilizer
The production process typically involves:
-
Raw Material Selection
Sourced from lignite, peat, or composted plant residues. -
Extraction and Concentration
Humic acid is extracted using alkaline solutions (e.g., potassium hydroxide) and separated from insoluble materials. -
Formulation and Granulation
The concentrated humic acid is blended with other nutrients (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus) and shaped into powder or granules. -
Drying and Packaging
Granules are dried, cooled, and packaged for distribution.
Some manufacturers incorporate beneficial microbes or additional organic matter, enhancing the fertilizer’s efficacy.
Benefits of Humic Acid Organic Fertilizer
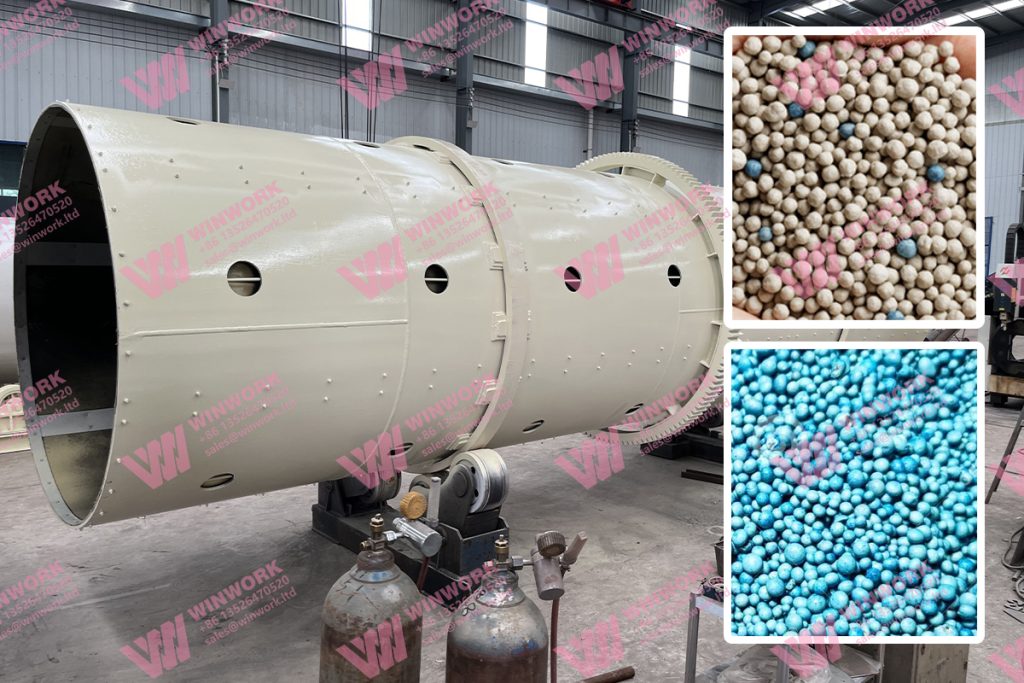

-
Improves Soil Structure
Enhances porosity and moisture retention in sandy soils while breaking up compacted clay soils. -
Boosts Fertilizer Efficiency
Reduces leaching of nutrients like nitrate and phosphate, improving uptake and minimizing environmental runoff. -
Increases Crop Yield and Quality
Studies show that crops treated with humic acid fertilizers often exhibit higher yield, better taste, and improved resistance to stress. -
Supports Soil Microbial Life
Encourages the growth of helpful bacteria and fungi that contribute to nutrient cycling. -
Eco-Friendly and Safe
Derived from natural sources, it supports organic farming practices and sustainable agriculture.
Applications in Agriculture

Humic acid organic fertilizer can be applied in various ways:
-
Base Fertilization: Applied before planting to prepare the soil
-
Top Dressing: Sprinkled around crops during growth stages
-
Foliar Spray: Diluted and sprayed on leaves for direct absorption
-
Drip Irrigation: Integrated into irrigation systems for efficient delivery
It is compatible with other fertilizers and pesticides, making it a versatile tool in integrated nutrient management programs.
Common Crop Applications
| Crop Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Grains (e.g., rice, wheat) | Promotes tillering and reduces lodging |
| Fruits (e.g., grapes, apples) | Enhances sugar content and size |
| Vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, lettuce) | Improves color, taste, and shelf life |
| Ornamentals | Encourages flowering and greener foliage |
Why Manufacturers Are Shifting to Humic Acid Fertilizer
With global soil degradation and over-fertilization concerns, fertilizer producers are turning to humic acid organic fertilizer as a sustainable alternative. Its organic certification potential makes it ideal for export markets and premium eco-labeled agricultural products.
Many fertilizer plants have added humic acid production lines alongside traditional compound fertilizer lines, integrating modern granulators, mixers, dryers, and automated packaging systems for high efficiency and consistent quality.
Case Study: A Fertilizer Company in Latin America
A fertilizer manufacturer in Brazil upgraded their production facility to include a humic acid organic fertilizer line using a rotary drum granulator, double shaft mixer, and automatic packaging machine. The outcome:
-
40% increase in organic fertilizer sales
-
Reduced customer complaints due to caking or uneven granulation
-
Entry into premium organic produce markets in Europe and Asia
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite its benefits, humic acid organic fertilizer faces challenges such as:
-
Raw Material Availability: High-quality humic sources like leonardite are limited.
-
Cost of Production: Processing and granulation increase overall costs.
-
Awareness Gap: Many farmers are still unfamiliar with its long-term benefits.
However, increasing demand for sustainable and certified organic inputs ensures a bright future for this product category.
Conclusion
As agriculture moves toward sustainability, humic acid organic fertilizer stands out as a key solution for soil restoration, crop productivity, and environmental protection. By integrating humic acid into their fertilization strategies, farmers and manufacturers alike can take meaningful steps toward eco-friendly, high-yield farming systems.
Whether you’re a grower seeking to improve soil health or a producer looking to expand your fertilizer line, humic acid is a technology worth investing in.






Get A Quote