Mushroom farming generates a significant amount of byproducts, particularly mushroom residue. This residue, typically consisting of leftover mushroom caps, stalks, and substrate, has long been considered waste. However, with the development of the mushroom residue organic fertilizer production line, this byproduct can now be transformed into a highly valuable, nutrient-rich organic fertilizer. Not only does this process contribute to reducing agricultural waste, but it also enhances soil fertility and promotes sustainable farming practices.
What is Mushroom Residue?

Mushroom residue refers to the leftover materials after the harvesting of mushrooms. These materials typically include the mushroom substrate (such as straw or sawdust), stems, caps, and any other residual organic matter that remains after mushrooms have been cultivated. Mushroom residue contains essential organic compounds, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as other micro-nutrients beneficial for plant growth. Instead of being discarded, mushroom residue can be processed into an organic fertilizer that enriches the soil.
Mushroom Residue Organic Fertilizer Production Line Process
The process of turning mushroom residue into organic fertilizer involves several key steps. Each step is designed to break down the organic matter and convert it into a nutrient-rich product suitable for agricultural use.

1. Collection and Preparation of Mushroom Residue
The first step in producing mushroom residue organic fertilizer is collecting the residue from mushroom farms. The residue, which is typically wet and bulky, needs to be properly dried to reduce moisture content. Drying is crucial for both ease of handling and preparation for fermentation. Once dried, the mushroom residue is ready for the next stage of processing.
2. Fermentation
After drying, the mushroom residue undergoes fermentation. In this process, beneficial microorganisms (such as bacteria and fungi) break down the complex organic compounds in the residue into simpler forms that are more easily absorbed by plants. Fermentation not only reduces pathogens but also enhances the nutritional value of the residue, making it an excellent soil amendment.
3. Blending with Other Organic Materials
To balance the nutrient composition of the fertilizer, the fermented mushroom residue is often mixed with other organic materials. These can include animal manure, plant residues, or compost. The blending of these materials ensures a balanced mix of nutrients—such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—resulting in a more complete fertilizer that supports healthy plant growth.
4. Granulation
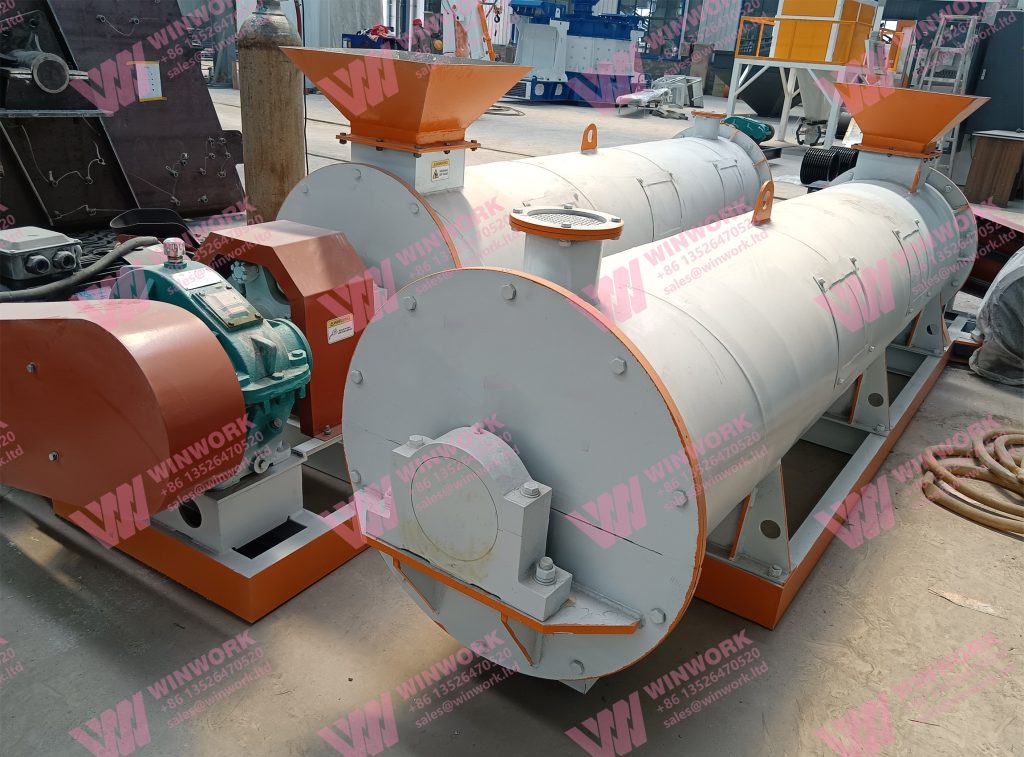

The blended organic materials are then fed into a fertilizer granulator. This machine compresses the mixture into small, uniform granules, making it easier to store, transport, and apply to crops. Granulation also ensures that nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the fertilizer, providing a controlled and consistent release of nutrients to plants.
5. Drying and Cooling
Once granulated, the fertilizer granules are dried to remove any remaining moisture. This step ensures that the final product is stable and can be stored for a longer period without clumping. After drying, the granules are cooled to maintain their structural integrity and prevent them from sticking together.
6. Screening and Packaging
After drying and cooling, the granules are screened to remove any oversized or undersized particles. The appropriately sized granules are then packaged using automatic packing machines, ready for sale or distribution. Packaging ensures that the mushroom residue organic fertilizer is easy to handle and store.
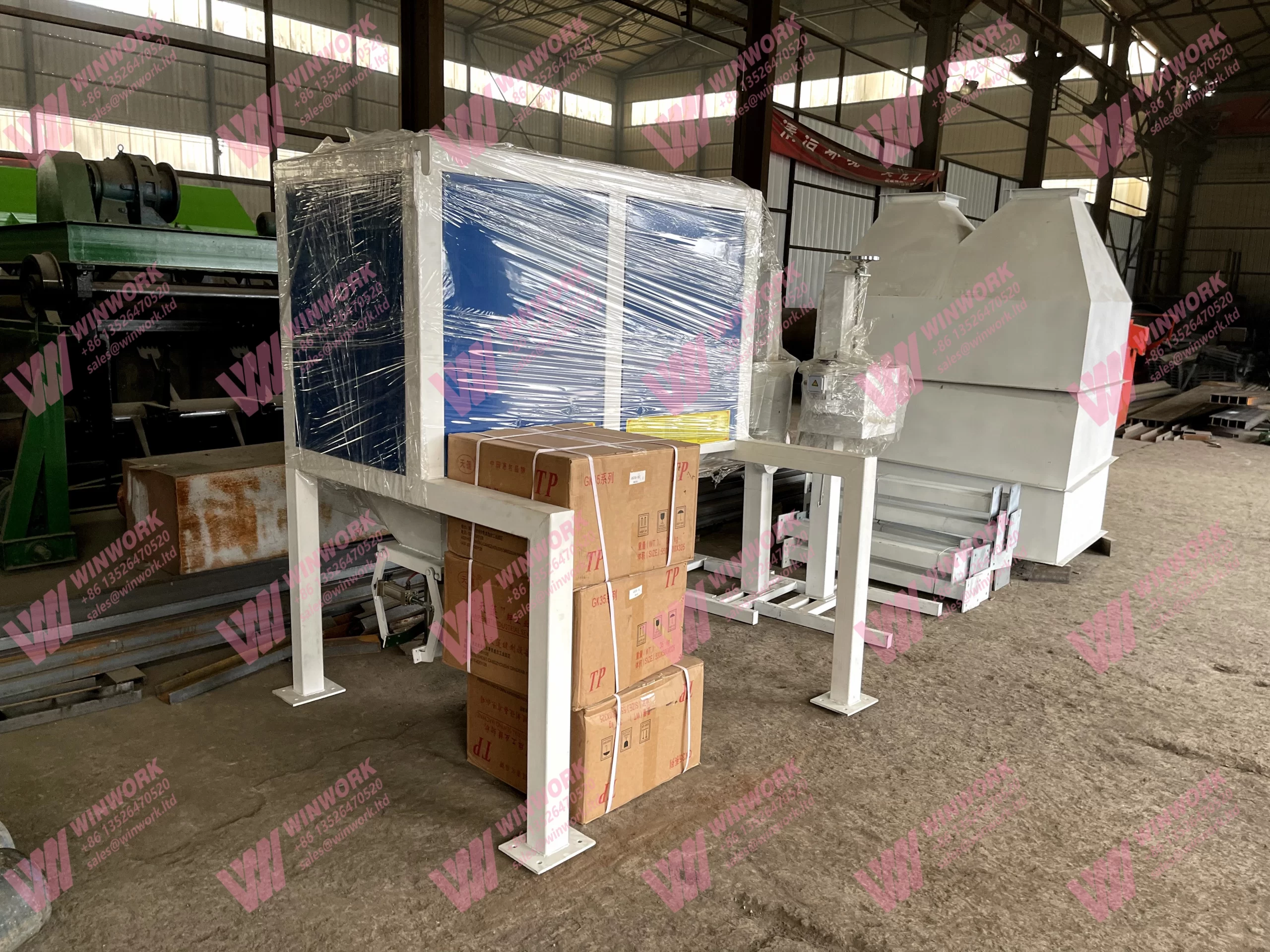
Key Equipment in Mushroom Residue Organic Fertilizer Production Line
The mushroom residue organic fertilizer production line includes several essential pieces of equipment:
- Fertilizer Granulator: A key piece of equipment that shapes the blended organic mixture into uniform granules, making it easier to apply and transport.
- Fertilizer Dryer: This equipment removes excess moisture from the granules to prevent clumping and ensure the fertilizer remains stable over time.
- Fertilizer Cooler: After drying, the cooler ensures that the granules maintain their shape and structure.
- Fertilizer Screening Machine: This machine screens the granules to remove any particles that are too large or too small, ensuring consistency in the final product.
- Automatic Packing Machine: Used to package the final product efficiently, ensuring that the fertilizer is ready for sale or use.
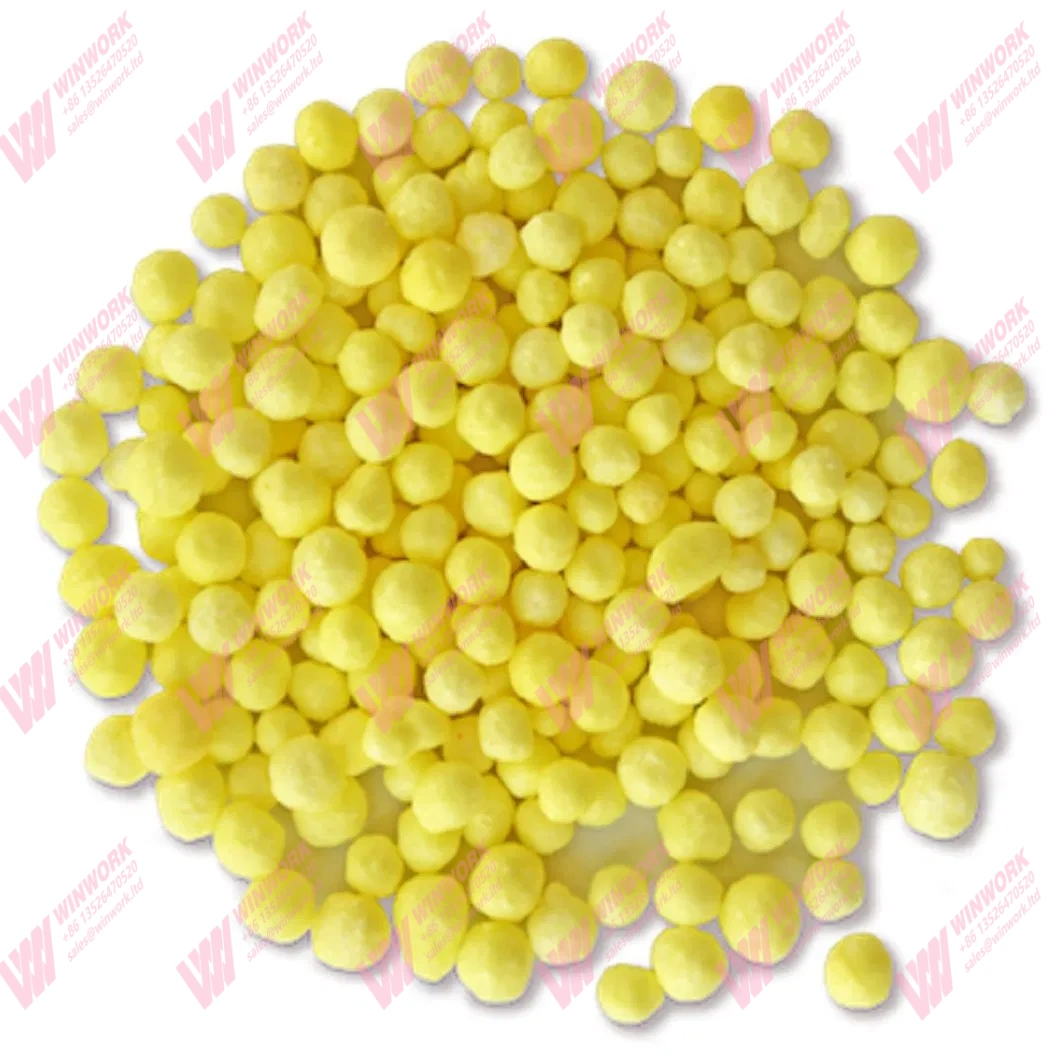
Benefits of Mushroom Residue Organic Fertilizer
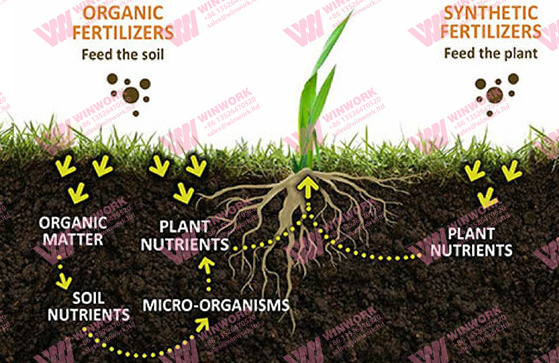
Converting mushroom residue into organic fertilizer offers numerous advantages for both farmers and the environment:
- Waste Reduction
By recycling mushroom residue into organic fertilizer, mushroom farms can significantly reduce waste, which would otherwise be disposed of in landfills or burned. This process turns agricultural byproducts into a valuable resource, supporting sustainable farming practices. - Rich Nutrient Content
Mushroom residue organic fertilizer is rich in essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are released slowly into the soil, providing plants with a steady supply of nourishment. This slow-release mechanism also reduces the risk of nutrient leaching, making it an eco-friendly option. - Improved Soil Health
Organic fertilizers like mushroom residue organic fertilizer improve soil structure by increasing microbial activity, enhancing water retention, and preventing soil erosion. Over time, this leads to healthier, more productive soil, which is crucial for long-term agricultural success. - Eco-Friendly and Sustainable
By using mushroom residue organic fertilizer, farmers reduce their reliance on chemical fertilizers, which can harm the environment and soil health. Organic fertilizers are biodegradable and non-toxic, making them a safer and more sustainable option for crop production. - Cost-Effective
Producing mushroom residue organic fertilizer is a cost-effective solution for mushroom farms. Instead of paying for waste disposal, farms can turn their byproducts into a valuable fertilizer that can be sold or used to enhance their own crop production.
How to Choose the Right Mushroom Residue Organic Fertilizer Production Line
When selecting a mushroom residue organic fertilizer production line, consider the following factors:
- Production Capacity: Choose a production line that suits your output needs, depending on the size of your mushroom farm and the amount of residue you generate.
- Customization: Look for a production line that allows customization of granule size, nutrient ratios, and other factors that meet your specific fertilizer requirements.
- Energy Efficiency: Opt for equipment that minimizes energy consumption to reduce operational costs and improve the overall sustainability of the production process.
- Quality Control: Ensure the production line includes quality control mechanisms to produce high-quality, consistent fertilizer.
Conclusion
The mushroom residue organic fertilizer production line offers a sustainable and efficient way to convert mushroom farming byproducts into valuable, nutrient-rich organic fertilizer. By recycling mushroom residue into fertilizer, farms can reduce waste, improve soil fertility, and contribute to more sustainable farming practices. This process not only benefits the environment but also provides a cost-effective solution for enhancing crop yields and promoting long-term agricultural success.






Get A Quote