In modern agriculture, the push for sustainability and efficiency has led to the growing demand for slow- and controlled-release fertilizers. Among these, Sulfur-Coated Urea (SCU) stands out as a smart nitrogen delivery system. A SCU fertilizer production line is designed specifically to manufacture these advanced fertilizers, ensuring gradual nutrient release, reduced losses, and optimized plant uptake. This article explores the key components, working principles, and advantages of an SCU fertilizer production line.
What is SCU Fertilizer?
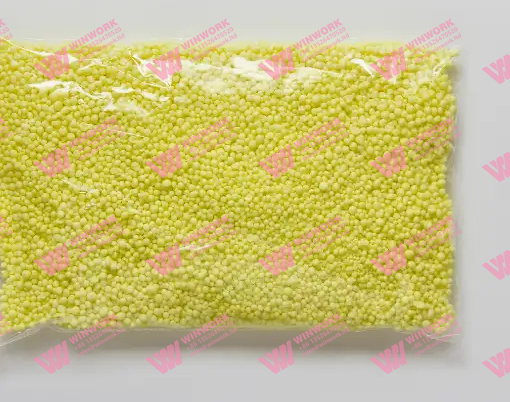

Sulfur-Coated Urea (SCU) is a type of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer. It consists of urea granules coated with a layer of elemental sulfur, sometimes enhanced with a wax or polymer sealant to further control nutrient release.
Key Benefits of SCU:
-
Extended nitrogen availability (up to 90 days)
-
Reduced nitrogen leaching and volatilization
-
Improved fertilizer use efficiency
-
Enhanced environmental protection
These advantages make SCU ideal for crops that benefit from stable nitrogen supply, including cereals, vegetables, fruit trees, and turfgrass.
Components of a SCU Fertilizer Production Line
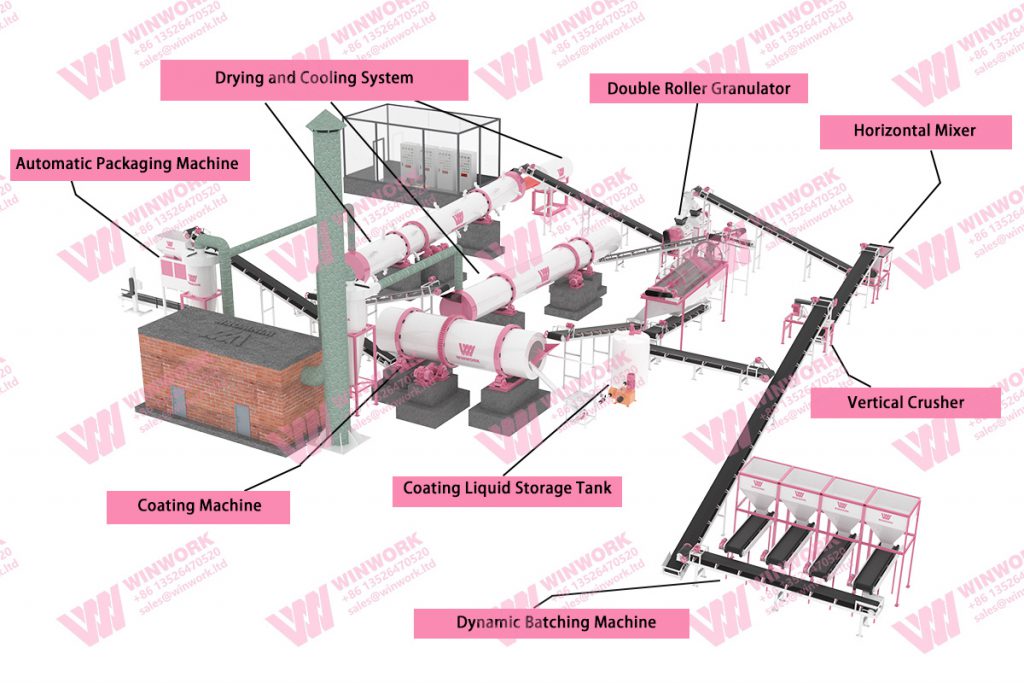
A standard SCU production line includes specialized machinery that ensures uniform sulfur coating, effective sealing, and consistent granule quality.
| Equipment | Function |
|---|---|
| Urea Preheater | Increases the temperature of urea for better coating adhesion |
| Sulfur Melting Tank | Melts sulfur to liquid form for even coating |
| Coating Drum | Applies molten sulfur onto urea granules |
| Polishing Drum | Smoothens coated granules and removes fines |
| Sealant Spray System | Adds wax/polymer layer to prevent cracks and moisture intrusion |
| Cooling System | Hardens coated granules quickly |
| Screening Machine | Sorts granules by size, returns off-spec to re-coating |
| Packing Machine | Automatically weighs, fills, and seals final product bags |
LANE’s SCU lines are customizable for capacities from 5 TPH to 20 TPH, depending on your production goals.
How the SCU Production Line Works

-
Urea Preparation
Urea granules are first preheated to 60–70°C to promote adhesion. -
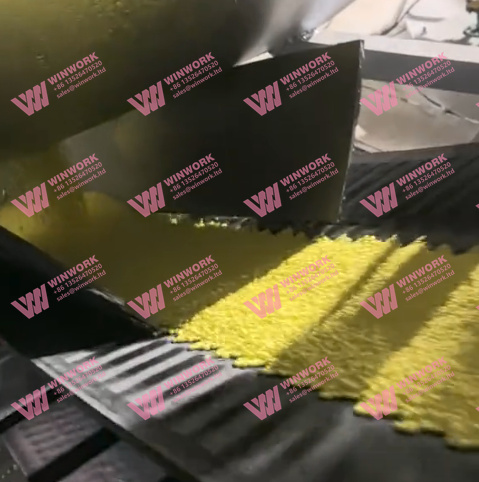
Sulfur Coating
Molten sulfur (120–150°C) is sprayed evenly onto the rotating bed of urea in the coating drum. This creates a uniform shell around each granule. -
Polishing and Sealing
Granules enter a polishing drum, where they are coated with a thin wax or polymer layer that seals pores and enhances moisture resistance. -
Cooling
A forced-air cooling system reduces the temperature quickly, helping the coating to harden and preventing sticking. -
Screening and Packaging
Final products are screened to meet size standards (typically 2–4 mm). Oversized and undersized granules are recycled. Qualified SCU is then packed and stored.
Features of LANE SCU Production Technology
-
High Sulfur Coating Uniformity: Precision control ensures uniform shell thickness from 5% to 15%.
-
Flexible Coating Ratios: Adjustable depending on crop needs and release duration.
-
Eco-Friendly Design: Emission control systems limit sulfur vapors and particulates.
-
Energy Efficiency: Heat recovery systems reuse process energy, reducing operational costs.
Why Invest in a SCU Fertilizer Production Line?
-
Market Demand Growth
Global SCU demand is rising due to stricter environmental regulations and sustainable agriculture initiatives. -
Premium Product Positioning
SCU fertilizers can be sold at a higher price due to their efficiency and eco-friendly profile. -
Reduced Application Frequency
Fewer applications per season reduce labor and logistics costs. -
Custom Formulations
You can integrate micronutrients or bio-stimulants into the SCU for added market value.
Comparison: SCU vs Conventional Urea
| Property | SCU | Urea |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen Content | ~36-37% | ~46% |
| Release Time | Up to 90 days | 3–7 days |
| Losses (Leaching/Volatilization) | Low | High |
| Application Frequency | 1–2 per season | 3–5 per season |
| Environmental Risk | Low | Moderate to high |
Though SCU has slightly lower nitrogen content, its slow-release performance dramatically improves nitrogen use efficiency, reducing overall fertilizer consumption by up to 30%.
Global SCU Applications
SCU fertilizer is widely used in:
-
Golf courses and turf management
-
Fruit orchards and vineyards
-
Vegetable farms
-
Forestry and ecological restoration
-
Controlled environment agriculture (CEA)
Case Study: 10 TPH SCU Line in Indonesia
A major Indonesian agribusiness deployed a 10-ton/hour SCU production line from us to meet the growing demand for slow-release fertilizers in palm oil plantations. Results within six months included:
-
25% fertilizer usage reduction
-
40% fewer application trips
-
Improved yield per hectare
-
Regulatory approval for export to the EU
Conclusion
A SCU fertilizer production line represents a forward-looking investment for any fertilizer manufacturer targeting sustainability, precision agriculture, and long-term profitability.
Contact us today to explore turnkey solutions for your SCU fertilizer production goals.






Get A Quote