As agriculture shifts toward sustainable practices, innovative fertilizers like sulfur coated urea (SCU) are gaining popularity for their efficiency and eco-friendliness. This advanced fertilizer offers a controlled release of nitrogen, reducing nutrient loss and minimizing environmental impact. At the heart of this innovation is sulfur coated urea production, a process that combines agricultural efficiency with sustainable practices. SCU ensures crops receive consistent nutrition while contributing to greener farming practices.
This article explores the production process, benefits, and environmental impact of sulfur coated urea, shedding light on how it aligns with the future of eco-friendly fertilization.
What is Sulfur Coated Urea?
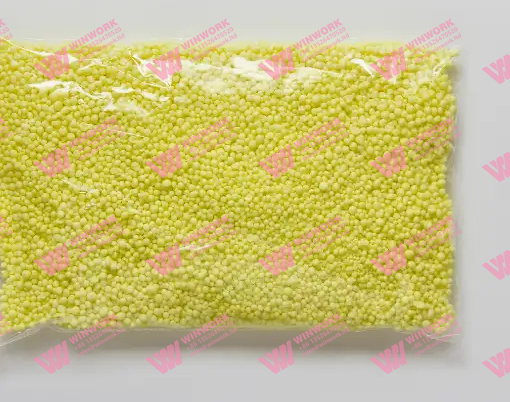

Sulfur coated urea (SCU) is a slow-release nitrogen fertilizer that improves nutrient uptake and minimizes nitrogen loss. It consists of urea granules coated with a layer of sulfur, which acts as a natural barrier, regulating the release of nitrogen into the soil.
SCU is designed to address one of the most common challenges in fertilization: the rapid loss of nitrogen through volatilization (gas release) and leaching (nutrient runoff). By controlling the release of nitrogen, Sulfur coated urea production ensures that crops receive a steady supply of nutrients over time, improving efficiency and reducing environmental pollution.
How Sulfur Coated Urea Production Works
The sulfur coated urea production process involves several key steps, each essential for creating high-quality fertilizer with consistent performance.
1. Raw Material Preparation
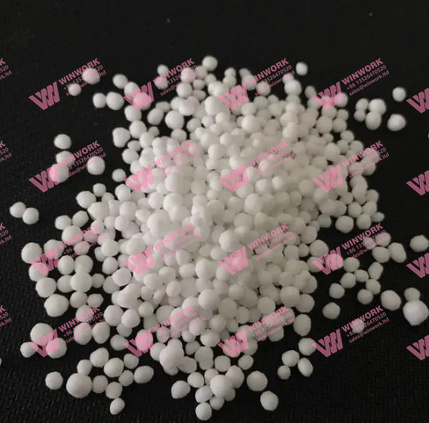

The production process begins with high-purity urea granules, which serve as the core of the fertilizer. The urea must meet strict quality standards to ensure uniform coating and nutrient release. Sulfur, often sourced from industrial byproducts, is prepared for use in the coating process.
2. Heating and Melting the Sulfur
Sulfur is melted at high temperatures to form a liquid that can be applied to the urea granules. The molten sulfur creates a thin, protective layer around each granule, controlling the release of nitrogen. Additives like waxes or polymers are sometimes used to improve the coating’s durability and prevent premature degradation.
3. Coating the Urea Granules
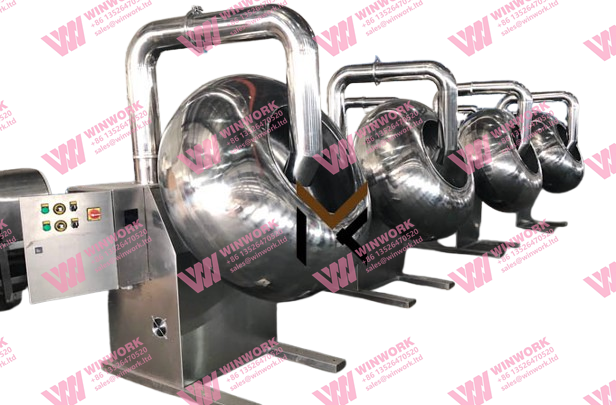

The molten sulfur is applied to the urea granules in rotating drum coaters or fluidized bed systems. As the granules rotate, they are evenly coated with sulfur, ensuring each granule is protected. Multiple layers can be applied to adjust the release rate of nitrogen based on the specific needs of crops and soil conditions.
4. Drying and Cooling
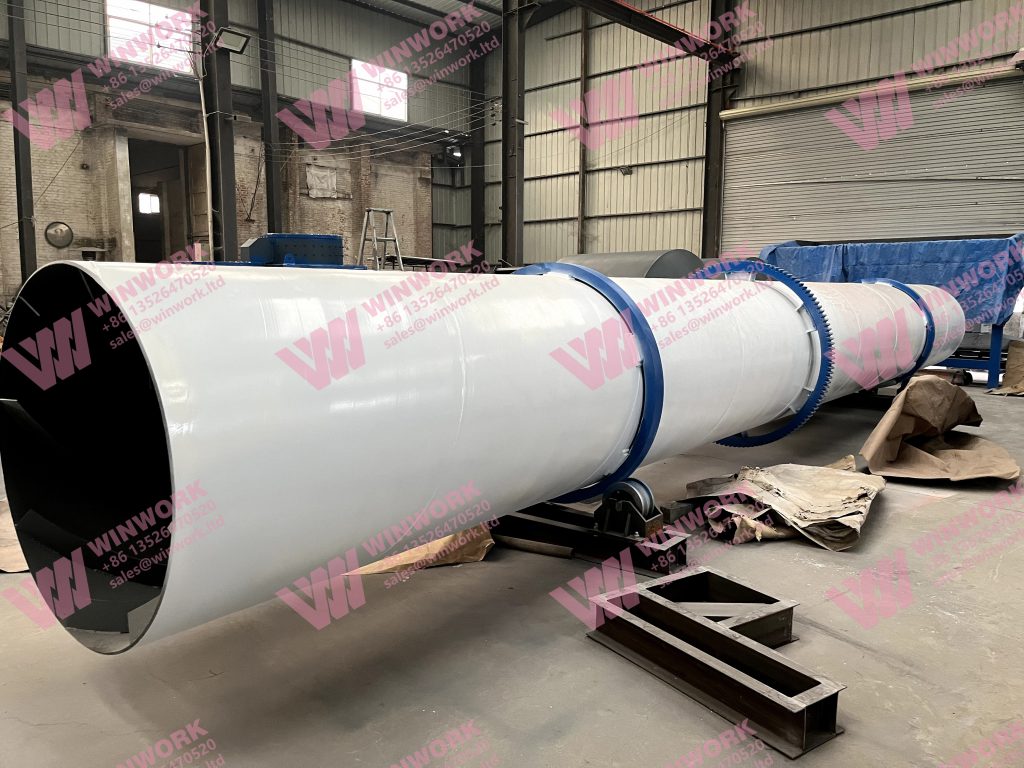

After coating, the granules are dried to remove moisture and cooled to ensure the sulfur layer solidifies properly. This step ensures the fertilizer remains stable during storage and transportation.
5. Screening and Packaging
The final product is screened to ensure uniform granule size and coating thickness. Any defective granules are removed, and the finished Sulfur coated urea production is packaged for distribution to agricultural suppliers and farmers.
The Benefits of Sulfur Coated Urea Production
1. Improved Nitrogen Use Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of SCU is its ability to improve nitrogen use efficiency. By releasing nitrogen gradually, Sulfur coated urea production ensures that plants receive consistent nourishment throughout their growth cycle, reducing the need for frequent fertilizer applications.
2. Reduced Environmental Impact
The controlled release of nitrogen minimizes nutrient losses through volatilization and leaching, reducing the risk of groundwater contamination and greenhouse gas emissions. This makes SCU an eco-friendly alternative to conventional nitrogen fertilizers.
3. Enhanced Crop Yields and Quality
Crops benefit from the consistent supply of nitrogen, which promotes healthy growth, robust root development, and improved yields. SCU is especially effective for crops with long growing cycles, such as cereals, fruits, and vegetables.
4. Sulfur Supplementation
In addition to nitrogen, SCU provides sulfur, an essential nutrient for crop metabolism. Sulfur improves protein synthesis and enhances the quality of produce, making SCU a valuable fertilizer for crops like oilseeds, legumes, and brassicas.
Eco-Friendly Practices in Sulfur Coated Urea Production
As sustainability becomes a priority in agriculture, manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices in sulfur coated urea production to reduce environmental impact and improve efficiency.
1. Sustainable Sourcing of Sulfur
Many SCU production facilities use sulfur sourced from industrial byproducts, such as those generated during petroleum refining. This practice reduces waste and promotes a circular economy by repurposing sulfur that would otherwise go unused.
2. Energy-Efficient Technologies
Modern production lines incorporate energy-efficient equipment, such as heat recovery systems, to minimize energy consumption during the coating process. Some facilities are also integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to further reduce their carbon footprint.
3. Reduction of Waste and Emissions
Innovative coating technologies ensure that minimal sulfur or urea is wasted during production. Emission control systems capture and recycle gases released during the process, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
4. Customization for Precision Agriculture
SCU production lines are increasingly focused on producing customized fertilizers tailored to specific crop needs. By adjusting the nitrogen release rate and sulfur content, manufacturers can create precision fertilizers that enhance nutrient efficiency and minimize waste.
Applications of Sulfur Coated Urea in Agriculture
1. Cereal Crops and Grains
SCU is widely used in the cultivation of wheat, rice, and corn, where consistent nitrogen supply supports vigorous plant growth and higher grain yields.
2. Fruit Orchards and Vineyards
In orchards and vineyards, Sulfur coated urea production ensures that fruit-bearing trees receive steady nutrition throughout the growing season, resulting in improved fruit quality and reduced nutrient stress.
3. Vegetable Farming
Vegetable crops such as tomatoes, lettuce, and peppers benefit from SCU’s ability to provide balanced nutrition, promoting uniform growth and minimizing nutrient deficiencies.
4. Oilseeds and Legumes
Sulfur is essential for crops like canola, soybeans, and alfalfa, which require both nitrogen and sulfur for optimal growth. SCU provides a reliable source of these nutrients, enhancing crop performance and yield.
Challenges and Solutions in SCU Production
While SCU offers numerous benefits, there are challenges associated with its production and use.
1. Production Costs
The coating process requires specialized equipment and energy-intensive operations, increasing production costs. However, advancements in energy efficiency and scaling up production can help reduce these costs over time.
2. Storage and Handling

SCU granules must be stored in dry conditions to prevent moisture absorption and degradation. Proper packaging and climate-controlled storage facilities ensure the fertilizer retains its effectiveness.
3. Market Awareness
Some farmers may hesitate to adopt SCU due to unfamiliarity with its benefits. Educational programs and field demonstrations can help promote the adoption of SCU and highlight its advantages over conventional fertilizers.
Conclusion
The future of fertilization lies in sustainable solutions that balance agricultural productivity with environmental responsibility. Sulfur coated urea production embodies this approach by delivering efficient nitrogen fertilizers that reduce nutrient loss, improve crop performance, and minimize environmental impact. With advancements in production technology and a growing focus on eco-friendly practices, SCU is set to play a pivotal role in the future of agriculture.
As farmers embrace precision agriculture and sustainable farming practices, Sulfur coated urea production will become an essential tool for meeting the world’s food demands while protecting natural resources. Through innovation and commitment to sustainability, the fertilizer industry is turning challenges into opportunities, shaping a greener and more productive future for global agriculture.






Get A Quote